Dataverse, CEDAR and RO-Crate: The building blocks of ARP, the federated research data repository of Hungary
13 October 2025 | By Balázs E. Pataki
The ARP Adatrepozitórium Platform (Data Repository Platform) is a national initiative of the Hungarian Research Network (HUN-REN), led by SZTAKI (HUN-REN Institute for Computer Science and Control), to build a multidisciplinary repository system capable of hosting the scientific data output of the Hungarian research community. ARP is a federated service that collects data from its own Dataverse repository as well as other institutional data repositories in Hungary to establish a European Open Science Cloud (EOSC)-compliant research infrastructure.
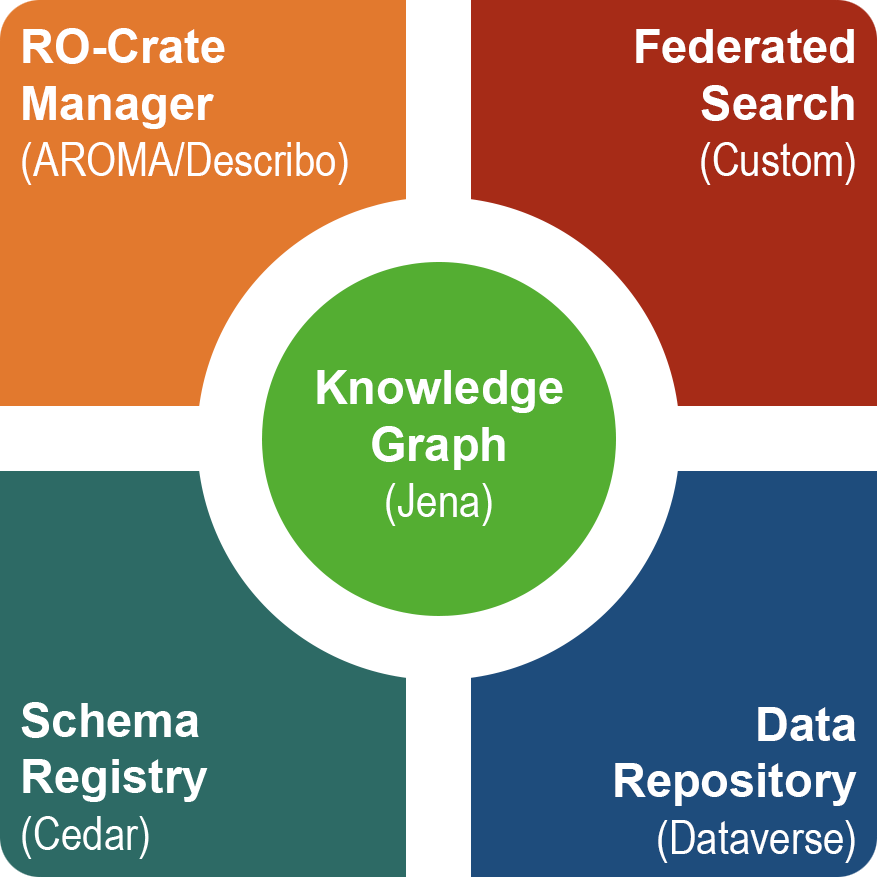
ARP is built around Harvard’s Dataverse. However, we found that to make ARP truly multidisciplinary, research communities need the ability to easily author and publish metadata schemas relevant to their scientific fields. While Dataverse provides metadata schemas via its metadata blocks and TSV input format, creating, updating, and curating these are challenging for researchers who are not metadata experts. To address this, we integrated Stanford’s CEDAR as the schema authoring registry tool for ARP. With this integration, researchers can now easily create complex schemas using CEDAR’s drag-and-drop template editor and export and synchronize these with Dataverse, effectively enabling direct metadatablock authoring within Dataverse.
Another limitation of Dataverse is that it provides only minimal metadata for the files within a dataset. To overcome this and enhance dataset accessibility, we introduced the Research Object Crate (RO-Crate) exchange format as a first-class object of ARP. We not only added export and import functionality for RO-Crate but also developed a complete authoring tool, AROMA , based on the RO-Crate editor component of the Describo project. The use of RO-Crate and the integration of CEDAR schemas make it possible to associate metadata not only with the root dataset but also with any files and subdirectories. Users can define their own specific schemas in CEDAR, associate them with selected files and directories of their dataset in AROMA, and use these schemas to describe their data in greater depth than was previously possible in Dataverse.
In this video we demonstrate how Dataverse, CEDAR, and RO-Crate enhance the metadata workflow of the Hungarian research community and how our achievements could be applied to the broader Dataverse community.

